DEPRESSION
There is often a confusion between having depression and feeling depressed. Almost everyone feels down at certain times in their lives due to some problems they may have in their lives. It can be after having an argument with someone, troubles at home or at work or anything that can cause a disappointment in one's life. Then, circumstance get better and alls well and the depresses feeling goes away. But sometimes feelings of depression don't go away. Depression is a mood disorder that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, an estimated 17 million adult Americans suffer from depression during any 1-year period.

The DSM-5 outlines the following criterion to make a diagnosis of depression. The individual must be experiencing five or more symptoms during the same 2-week period and at least one of the symptoms should be either (1) depressed mood or (2) loss of interest or pleasure.
- Depressed mood most of the day, nearly every day.
- Markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all, or almost all, activities most of the day, nearly every day.
- Significant weight loss when not dieting or weight gain, or decrease or increase in appetite nearly every day.
- A slowing down of thought and a reduction of physical movement (observable by others, not merely subjective feelings of restlessness or being slowed down).
- Fatigue or loss of energy nearly every day.
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive or inappropriate guilt nearly every day.
- Diminished ability to think or concentrate, or indecisiveness, nearly every day.
- Recurrent thoughts of death, recurrent suicidal ideation without a specific plan, or a suicide attempt or a specific plan for committing suicide.

Depression has many different types. Here is a list of the types of depression.
- Major depressive disorder
- Bipolar disorder
Four sub-types of Bipolar Disorder
a) Bipolar I Disorder
- where the individual has experienced a minimum of one manic episode (lasting at least 7 days), it's not necessary to experience a depressive episode to diagnose Bipolar I
b) Bipolar II Disorder
- where the individual has experienced at least one major depressive episode (lasting two weeks) as well as a hypomanic episode (lasting at least 4 days)
c) Cyclothymia
- where the individual has experienced a combination of depressive and hypomanic episodes, the episodes are short but shift frequently
d) Other
- when bipolar depression is present but does not fall under the categories listed above.
- Dysthymia
Also called Persistent depressive disorder, is a continuous long-term (chronic) form of depression. You may lose interest in normal daily activities, feel hopeless, lack productivity, and have low self-esteem and an overall feeling of inadequacy. These feelings last for years and may significantly interfere with your relationships, school, work and daily activities.
If you have persistent depressive disorder, you may find it hard to be upbeat even on happy occasions — you may be described as having a gloomy personality, constantly complaining or incapable of having fun. Though persistent depressive disorder is not as severe as major depression, your current depressed mood may be mild, moderate or severe.
Because of the chronic nature of persistent depressive disorder, coping with depression symptoms can be challenging, but a combination of talk therapy (psychotherapy) and medication can be effective in treating this condition.
- Psychotic depression
Psychotic depression is a subtype of major depressive disorder (MDD). It is also referred to as MDD with psychotic features.
Psychotic depression symptoms are the same as those of MDD, such as feeling sad, listlessness, and having sleep problems, but they also include symptoms of psychosis. The hallmark symptoms of psychosis are hallucinations and delusions.
- Hallucinations: Sensory experiences not based in reality, such as seeing, hearing, tasting, feeling (through touch), or smelling things that are not really there and that others cannot sense.
- Delusions: Persistent false beliefs that are not grounded in reality, such as paranoia, a sense that someone is trying to harm you.
Psychosis can also occur with certain medications, substance use, or other health problems.
- Situational depression

- Seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
- Postpartum depression
SSRI - Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Depression may be caused by low levels of serotonin (also called the feel good chemical) in the brain that causes individual's to feel relaxed. Serotonin circulates in the brain before being absorbed by the bloodstream. SSRIs work by preventing your blood from absorbing some of the serotonin from your brain. Therefore leaves more serotonin available to work in your brain which can relieve depression. Some examples are sertraline (Zoloft), fluoxetine (Prozac), citalopram (Cilift), escitalopram (Cipramil), paroxetine (Paxil), fluvoxamine (Luvox). However these can cause some side effects example, diarrhoea, weight gain, sexual dysfunction, tiredness, nausea, dry mouth, headache, rash, sweating, nervousness, trouble sleeping.
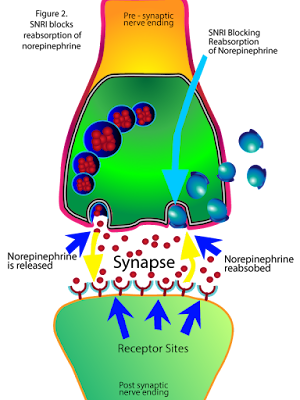
SNRI - Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
COUNSELLING
Counselling is often the first form of treatment recommended for depression. The person with depression talks to a licensed and trained mental healthcare professional example a psychologist who helps the person identify and work through the factors that may be triggering the depression through psychotherapy.
Sometimes these factors work in combination with heredity or chemical imbalances in the brain to trigger depression. Taking care of the psychological and psychosocial aspects of depression are just as important as treating its medical cause. Psychotherapy helps the client to regain a sense of control and pleasure in life again by understanding and identifying the life problems and events that contribute to their depression. This can help them to understand which aspects of those problems they may be able to solve or improve. They also help in understanding the behaviours, emotions, and ideas that contribute to his or her depressed state. By gaining all this understanding, the individuals learn coping techniques and problem-solving skills.



















No comments:
Post a Comment